Calling Web Service in Elm
This time we will call the LanguageTool proofreading service to check the entered text.
We will look at commands, HTTP requests, and working with JSON in Elm. Feel free to look into the elm guide for an overview of these features.
The source code for this post is available in the 05-calling-proofread-service folder in the elm-proofreading repository.
Changing from beginnerProgram to program
Before we can make HTTP requests, there is one thing we need to do. That is, update our main, which is a description of our application, from Html.beginnerProgram to Html.program.
Here are our old and new main configurations:
-- Old
main : Program Never Model Msg
main =
Html.beginnerProgram
{ model = model
, view = view
, update = update
}
-- New
main : Program Never Model Msg
main =
Html.program
{ init = init
, view = view
, update = update
, subscriptions = subscriptions
}Let’s look at new parts.
New update function
In Elm we don’t perform HTTP requests, or any other action with side effects, directly in our code. Instead, we pass the Elm framework a Command that describes what action should be performed and what message should come back into our application once it’s done.
So we need a way to pass commands to Elm. Right now, our update function takes a message and a model, and returns Elm a new model. Thus its signature is the following:
update : Msg -> Model -> ModelWhen we switch main to be Html.program, the update function it requires would be:
update : Msg -> Model -> (Model, Cmd Msg)The input parameters would stay the same—a message and the model, but the output would become a tuple. This tuple contains a new model, and a command we would like Elm to perform for us.
This new version of the update function will allow us to perform HTTP requests.
init and subscriptions functions
There are two new functions that we need to specify for our new main program:
initfunction returns an initial state of the application.subscriptionsfunction returns a description of subscriptions needed by an app. We won’t use subscriptions for our application.
Now with an updated main description, we can start implementing proofreading.
Adding Proofread Button
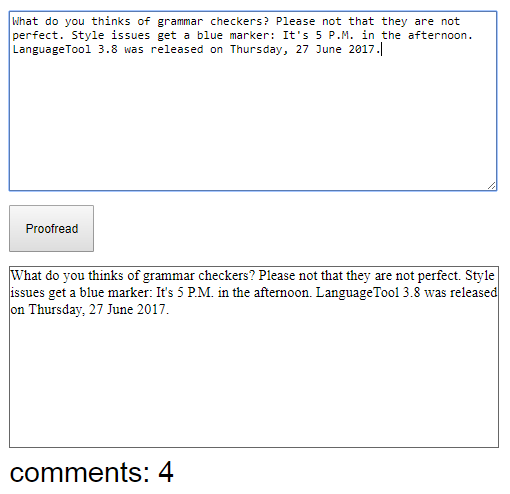
I will add a button to a page, that will initiate proofreading. Here’s the updated code for the view function:
view : Model -> Html Msg
view model =
div []
[ textarea [ onInput SetText, value model.text, class "text-editor" ] []
, button [ onClick Proofread ] [ text "Proofread" ]
, div [ class "proofread-panel" ] [ text model.text ]
]Using onClick attribute I specify, that clicking on the button will trigger the Proofread message. I added this message to the Msg type along with the case branch in the update function:
type Msg
= SetText String
| Proofread
update : Msg -> Model -> ( Model, Cmd Msg )
update msg model =
case msg of
SetText text ->
( { model | text = text, comments = [] }, Cmd.none )
Proofread ->
( model, requestProofread model.text )In case of SetText message, we change our model with new text and return Cmd.none to signal Elm that there are no commands to run.
In case of Proofread message, we return the same model, but there is a command that we want to perform. It is returned by our requestProofread function.
LanguageTool Web Service
LanguageTool API provides a check operation that checks the text for style and grammar issues. It requires two parameters:
text—a text to check, we will pass entered text here.language—language of passed text, this will be"en-US"in our case.
To get a proofread result we need to POST a request to https://languagetool.org/api/v2/check with specified parameters.
The response will contain among other information a list of messages, that describe possible issues. For simplicity sake, we will get only a part of information. For each message we will get:
message—description of an issue;offset—starting index of the problematic word or phrase;length—length of the problematic word or phrase.
Having this information would be enough to highlight problematic places in text and provide some additional context on an issue.
Here is an example of a JSON structure we expect to get from the service. All the other data from the response will be skipped:
{
"matches": [
{
"message": "Possible spelling mistake found",
"offset": 0,
"length": 7
},
{
"message": "Don't put a space before the closing parenthesis",
"offset": 9,
"length": 11
}
]
}Making HTTP Request
I’ve mentioned already that we are not going to call proofreading web service directly.
We need to create a Command that will contain the details of a call that should be performed, and a message that should be called afterward. We will pass this Command to Elm to perform, and Elm will pass us the result of a call with a message in the update function.
Updating model
Before making a request, we need to update our data model. I’ll add a Comment alias for a record that describes comments from the proofread service and update the model to store a list of such comments.
type alias Comment =
{ message : String
, offset : Int
, length : Int
}
type alias Model =
{ text : String
, comments : List Comment
}Updating Msg messages
Now, let’s add a ProofreadResult message that should happen when Elm will perform our request. It will contain the Result type with either a request error or a list of comments.
type Msg
= SetText String
| Proofread
| ProofreadResult (Result Http.Error (List Message))Creating Http request
Here is the code for creating our request to the service. I’ll show it all, and after that we’ll take a look at details:
requestProofread : String -> Cmd Msg
requestProofread text =
let
url =
"https://languagetool.org/api/v2/check"
body =
Http.stringBody "application/x-www-form-urlencoded" (encodeProofreadRequest text)
request =
Http.post url body commentListDecoder
in
Http.send ProofreadResult request
encodeProofreadRequest : String -> String
encodeProofreadRequest text =
String.join "&"
[ "text=" ++ Http.encodeUri text
, "language=" ++ "en-US"
]
commentDecoder : Decoder Comment
commentDecoder =
map3 Comment
(field "message" string)
(field "offset" int)
(field "length" int)
commentListDecoder : Decoder (List Comment)
commentListDecoder =
at [ "matches" ] (list commentDecoder)To create a command in the requestProofread function we’re calling Http.send function that gets a request and a message ProofreadResult to call afterward.
The request is created with the Http.post function. It takes the following parameters:
url—a service method URL;body—a header and required parameters for a service call—textandlanguage;messageListDecoder—a description for Elm on how to convert the JSON from the response into Elm objects. In our casemessageListDecoderdescribes how to get a list ofMessagerecords from JSON.
Processing request result
The created command is passed to Elm in the update function. Elm performs the command and calls a web service. After that, Elm calls our update function with ProofreadResult message that contains the result of a request:
update : Msg -> Model -> ( Model, Cmd Msg )
update msg model =
case msg of
...
ProofreadResult (Ok messages) ->
( { model | comments = messages }, Cmd.none )
ProofreadResult (Err error) ->
( model, Cmd.none )If the request succeeded, ProofreadResult will contain a list of messages. In this case, we update our model with this list.
If something went wrong, we’ll get an error description. In this case, we just return the same model.
In the view function, I’ve added the viewCommentsCount function that will render a number of comments we received.
In the next post, we’ll show the proofreading results in a more friendly way.